杂题记录
1838. 最高频元素的频数
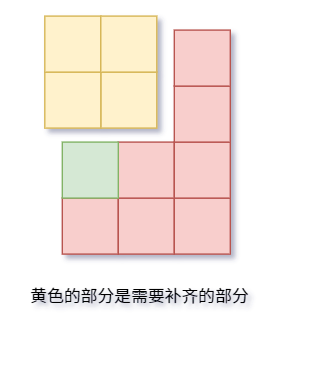
题目的要求是,在给定的元素内,使数组齐平。例如下图是一个 [1,2,4] 的数组,当 k = 5时补齐的状态。所以答案为 3 。
所以可以使用一个滑动窗口,在这个滑动范围之内,都会尝试去用 k 将数组补齐。要使用滑动窗口,必须先让它排个序!此时已经是 (nlogn)了。
由于排序数组了,每次枚举在区间内最大的数,会尝试用 k 去补齐。在滑动循环内只能由两种情况:(假设滑动区间为 left ~ right)
- 尝试将区间的数向
nums[right]补齐,使用的次数sum小于等于k。
直接更新当前答案。
// 此刻之前的元素已经与 nums[right - 1] 补齐
// 所以现在只需要把之间的差补齐
nums += (nums[right] - nums[right - 1]) * (right - left);
res = Math.max(res, right - left + 1);
- 尝试将区间的数向
nums[right]补齐,使用的次数sum大于k。
这种情况不符合题目题意,需要收缩窗口。
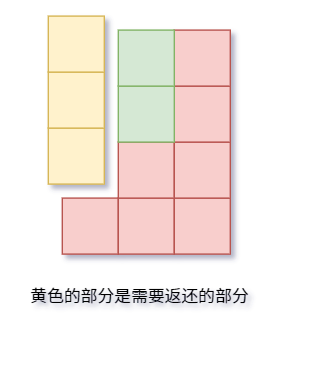
第一步:将 left 向 nums[right] 补齐时所占的次数返回,即 sum - <所占部分>。第二步:将 left + 1。
sum -= nums[right] - nums[left];
完整JavaScript代码:
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @param {number} k
* @return {number}
*/
var maxFrequency = function(nums, k) {
nums.sort((a, b) => a - b);
let res = 1;
let [left, right, sum] = [0, 1, 0];
for (; right < nums.length; ++ right) {
sum += (nums[right] - nums[right-1]) * (right - left);
while (sum > k) {
sum -= nums[right] - nums[left];
left++;
}
res = Math.max(res, right - left + 1);
}
return res;
};
剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点
输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共节点。

解题思路和动图均来自:leetcode-腐烂的橘子
我们使用两个指针 node1,node2 分别指向两个链表 headA,headB 的头结点,然后同时分别逐结点遍历。
当 node1 到达链表 headA 的末尾时,重新定位到链表 headB 的头结点;
当 node2 到达链表 headB 的末尾时,重新定位到链表 headA 的头结点;
这样,当它们相遇时,所指向的结点就是第一个公共结点。

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} headA
* @param {ListNode} headB
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var getIntersectionNode = function(headA, headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
let [p1, p2] = [headA, headB];
while (p1 !== p2) {
p1 = p1 === null ? headB : p1.next;
p2 = p2 === null ? headA : p2.next;
}
return p1;
};
138. 复制带随机指针的链表
思路:
- 先在原链表上进行复制(蓝色是旧的,黄色是新的)
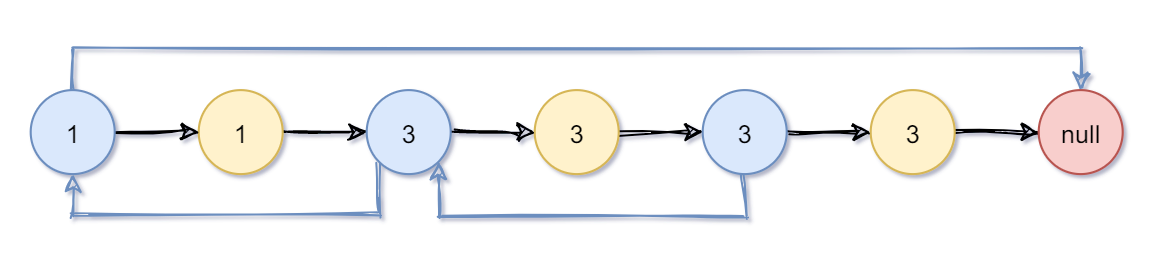
- 我们先让random指向原链表中的。
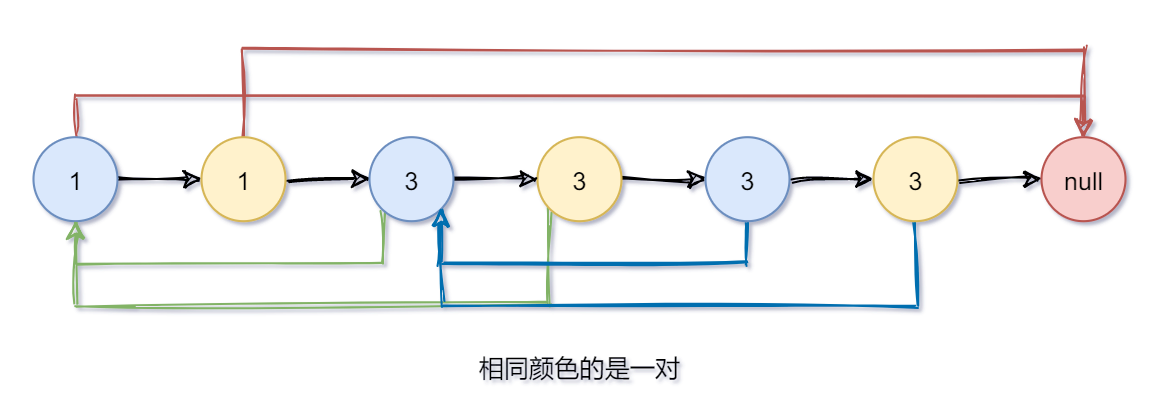
- 统一让新节点的random指向原链表中的下一个节点,就是random的新节点了。
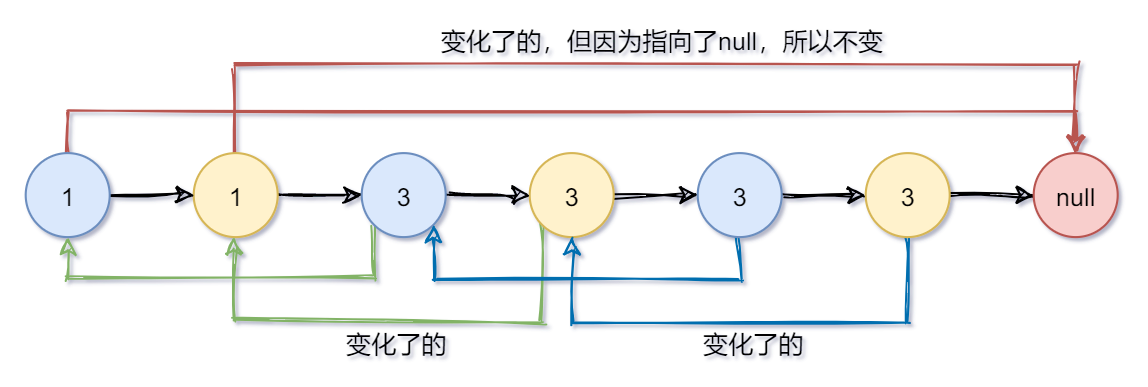
- 最后再进行分裂
比如 node.next = node.next.next ,就是直接越过一个节点(越过新节点直接指向旧节点)。
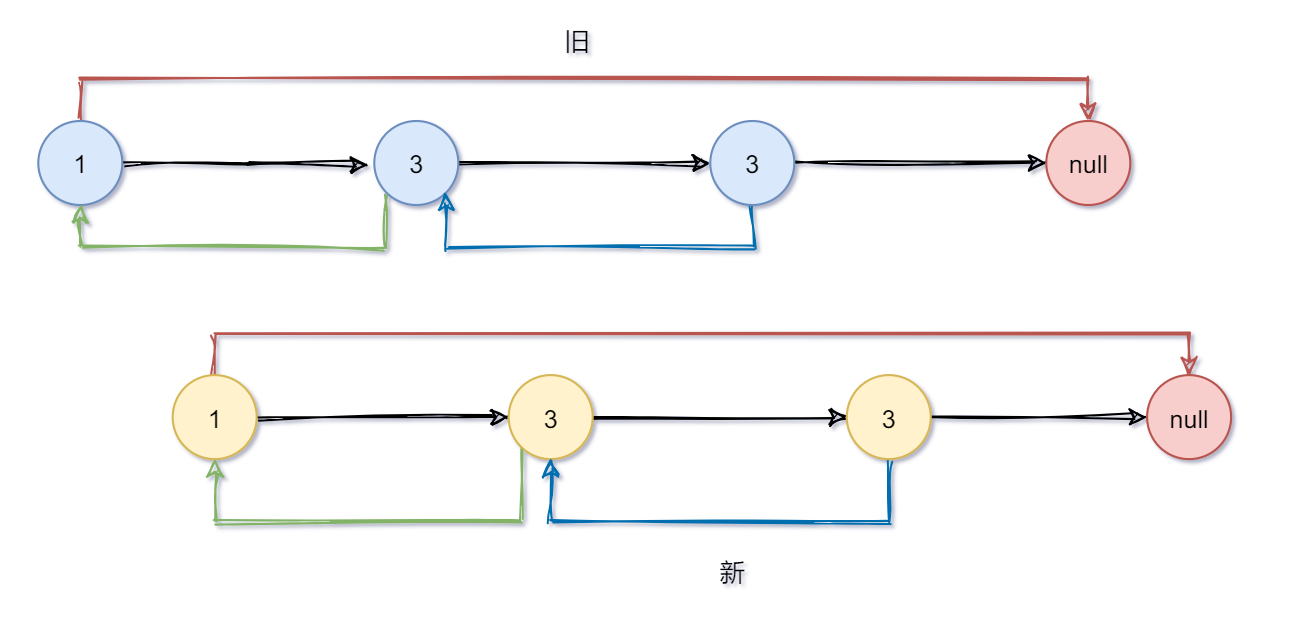
/**
* // Definition for a Node.
* function Node(val, next, random) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = next;
* this.random = random;
* };
*/
/**
* @param {Node} head
* @return {Node}
*/
var copyRandomList = function(head) {
if (head === null) return null;
// 复制一份
for (let node = head; node; node = node.next.next) {
const newNode = new Node(node.val, null, node.random);
newNode.next = node.next;
node.next = newNode;
}
// 复制random链表
for (let node = head; node; node = node.next.next) {
const newNode = node.next;
newNode.random = newNode.random ? newNode.random.next : null;
}
// 分裂
// 还原原来的链表、将新链表分离出去
const res = head.next;
for (let node = head; node; node = node.next) {
const newNode = node.next;
node.next = node.next ? node.next.next : null;
newNode.next = newNode.next ? newNode.next.next : null;
}
return res;
};
1893. 检查是否区域内所有整数都被覆盖
再回忆一下差分。
- 差分求前缀和 -> 得到原数组
- 在一段区间内的数组元素都加上一个数
c->diff[left] += c; diff[right+1] -= c
这道题的 ranges 每个元素给的都是一个区间的 left 和 right,接着把 1 当成上面式子的 c,这样就能把 left 到 right之间的数出现次数 +1了。
下图的 ranges 数组已经给出,diff 是差分数组,prefix 是前缀和数组,它也代表每个元素出现的次数。
index 标红的数字即为满足条件的下标。
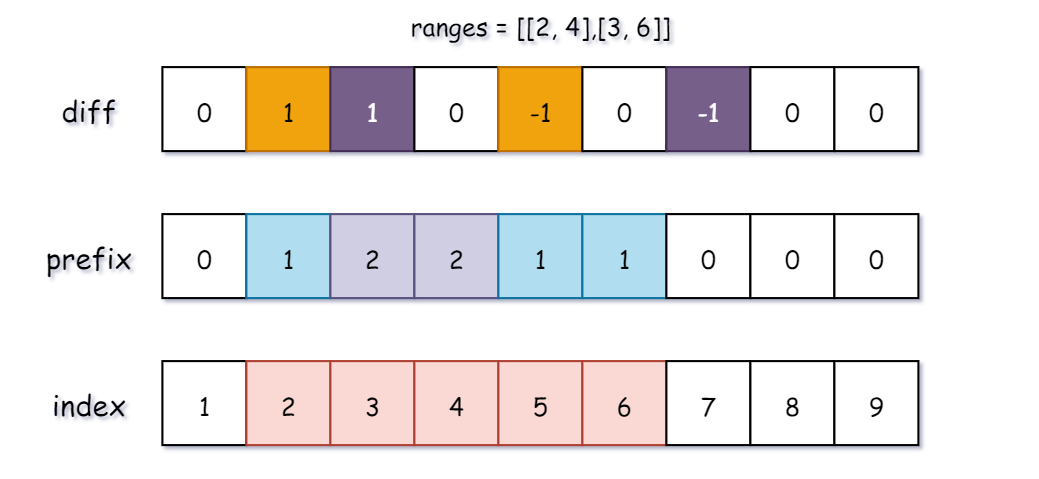
所以思路就是先构造差分数组,通过差分数组去构造前缀和数组,求出每个数组出现的频率。
最后再从 left 遍历到 right,如果都满足就返回 true 就可以了。
/**
* @param {number[][]} ranges
* @param {number} left
* @param {number} right
* @return {boolean}
*/
var isCovered = function(ranges, left, right) {
const diff = createZeroArray(60);
// 构造差分数组
ranges.forEach(x => {
diff[x[0]] = diff[x[0]] + 1;
diff[x[1] + 1] = diff[x[1] + 1] - 1;
});
// 差分数组求前缀和就是每个数字出现的次数
const prefix = createZeroArray(60);
for (let i = 1; i <= 51; ++ i) {
prefix[i] = diff[i] + prefix[i-1];
}
for (let i = left; i <= right; ++ i) {
if (prefix[i] === 0) return false;
}
return true;
};
function createZeroArray(size){
const res = [];
res.length = size;
res.fill(0, 0, size);
return res;
}
剑指 Offer 07. 重建二叉树
输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请构建该二叉树并返回其根节点。
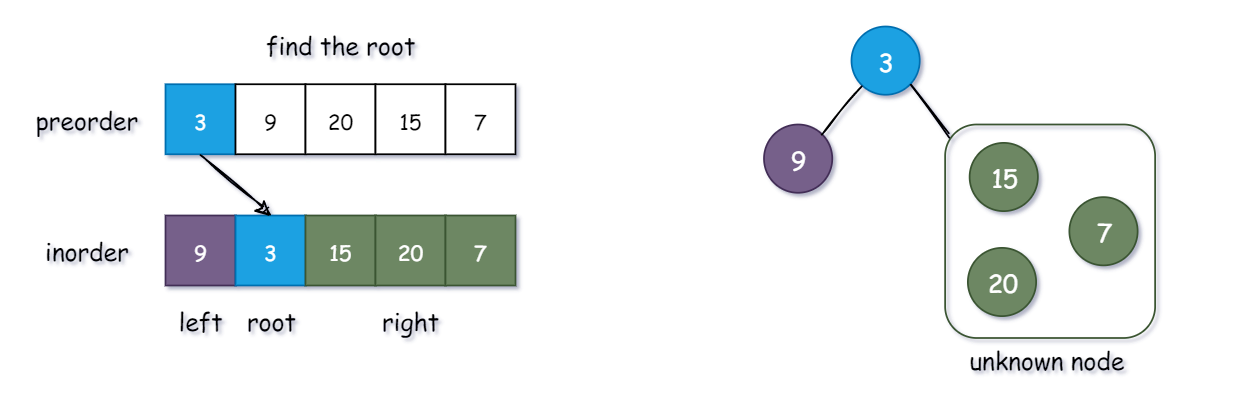
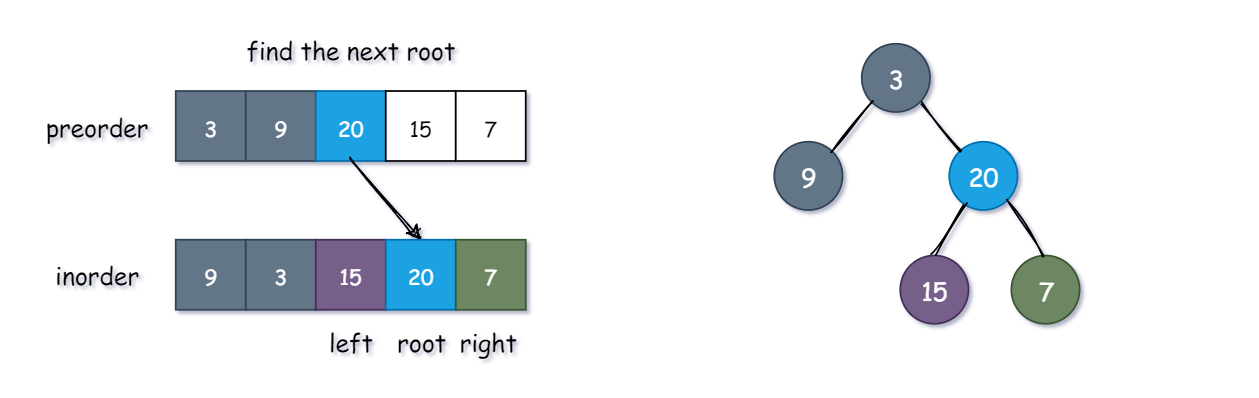
知识点:
- 前序遍历列表:第一个元素永远是 【根节点 (root)】
- 中序遍历列表:根节点 (root)【左边】的所有元素都在根节点的【左分支】,【右边】的所有元素都在根节点的【右分支】
算法思路:
- 通过【preorder】确定【根节点 (root)】
- 将【inorder】的节点分割成【left】和【right】
- 递归寻找【left】中的【根节点 (left root)】和 【right】中的【根节点 (right root)】
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {number[]} preorder
* @param {number[]} inorder
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var buildTree = function (preorder, inorder) {
if (preorder == 0) return null;
const tree = new TreeNode(preorder[0]);
const divideIdx = inorder.indexOf(tree.val);
const leftPre = preorder.slice(1, divideIdx + 1);
const leftIn = inorder.slice(0, divideIdx);
const left = buildTree(leftPre, leftIn);
const rightPre = preorder.slice(divideIdx + 1);
const rightIn = inorder.slice(divideIdx + 1);
const right = buildTree(rightPre, rightIn);
tree.left = left, tree.right = right;
return tree;
};
剑指 Offer 04. 二维数组中的查找
题解来自:leetcode-Krahets
我们将矩阵逆时针旋转 45° ,并将其转化为图形式,发现其类似于二叉搜索树 ,即对于每个元素,其左分支元素更小、右分支元素更大。因此,通过从 “根节点” 开始搜索,遇到比 target 大的元素就向左,反之向右,即可找到目标值 target 。
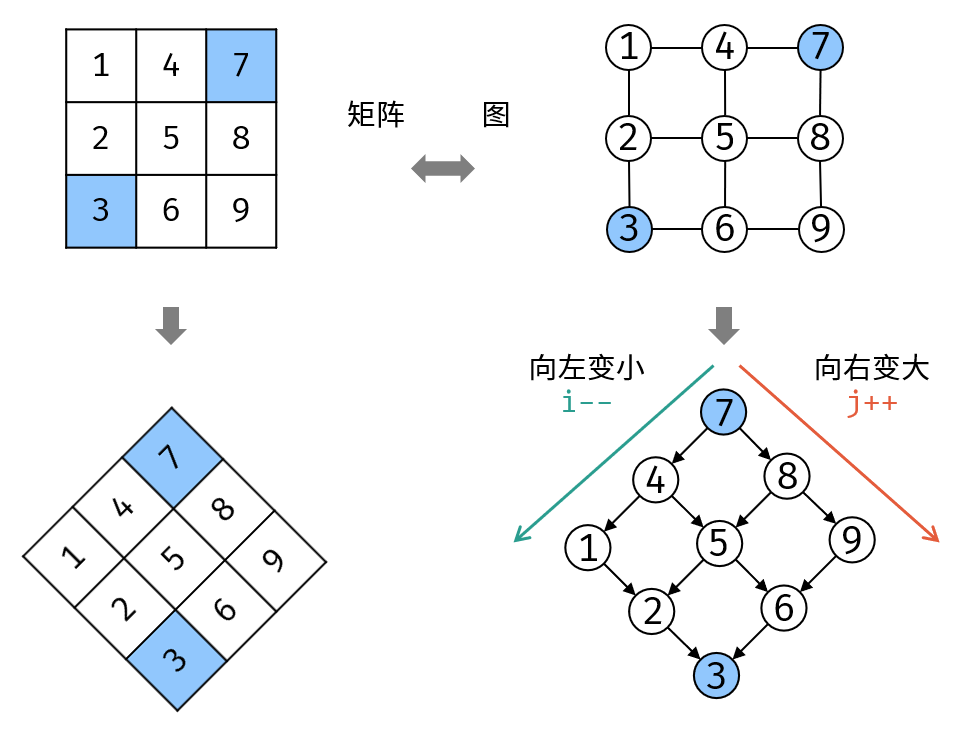
算法流程:
从矩阵 matrix 左下角元素(索引设为 (i, j) )开始遍历,并与目标值对比:
- 当
matrix[i][j] > target时,执行i--,即消去第i行元素; - 当
matrix[i][j] < target时,执行j++,即消去第j列元素; - 当
matrix[i][j] = target时,返回true,代表找到目标值。
若行索引或列索引越界,则代表矩阵中无目标值,返回 false 。
/**
* @param {number[][]} matrix
* @param {number} target
* @return {boolean}
*/
var findNumberIn2DArray = function(matrix, target) {
let [x, y] = [matrix.length - 1, 0];
while (x >= 0 && y < matrix[0].length) {
const now = matrix[x][y];
if (now > target) x--;
else if (now < target) y++;
else return true;
}
return false;
};
L1-050 倒数第N个字符串 (15 分)
十进制与二十六进制相互转换
L1-6 福到了 (15 分)
getchar(); // 读取上一行换行符
getline(cin, str); // 读取一行到 string str 中
L2-3 名人堂与代金券 (25 分)
结构体数组排序
struct student {
string email;
int score;
bool operator< (const student &S) const {
if (score != S.score) return score > S.score; // 成绩降序
else return email < S.email; // 邮箱升序
}
}stu[N];
// ......
sort(stu, stu + n);
L2-028 秀恩爱分得快 (25 分)
bool exitsA = find(pic[i].begin(), pic[i].end(), aId) != pic[i].end();
L1-042 日期格式化 (5 分)
整数前补 0
printf("%d-%02d-%02d", y, m, d);
L1-3 阅览室 (20 分)
unordered_map 判断存在和删除
m.count(id); // exist
m.erase(id); // delete
L1-048 矩阵A乘以B (15 分)
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9 0
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
res
1 * 7 + 2 * 1 + 3 * 5 | 1 * 8 + 2 * 2 + 3 * 6 | 1 * 9 + 2 * 3 + 3 * 7 | 1 * 0 + 2 * 4 + 3 * 8
4 * 7 + 5 * 1 + 6 * 5 | 4 * 8 + 5 * 2 + 6 * 6 | 4 * 9 + 5 * 3 + 6 * 7 | 4 * 0 + 5 * 4 + 6 * 8
L2-024 部落 (25 分)
并查集树的数目可以用 unordered_map 的 size 来表示
L3-029 还原文件 (30 分)
字符串哈希 + 深搜拼接
2203. 得到要求路径的最小带权子图
tip
dijkstra 函数式写法
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
#define x first
#define y second
#define N 100010
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f
class Solution {
public:
LL dist1[N], dist2[N], dist3[N];
int st[N];
LL res = INF;
vector<PII> head[N], back[N];
void dijkstra(int n, int start, vector<PII> * node, LL * dist) {
memset(st, 0, sizeof st);
priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII>> heap;
dist[start] = 0;
st[start] = 1;
heap.push({0, start});
while (heap.size()) {
PII the = heap.top();
heap.pop();
int p = the.y;
int w = the.x;
if (st[p] == 0) continue;
st[p] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < node[p].size(); ++ i) {
int nextp = node[p][i].y;
int nextw = node[p][i].x;
if (dist[p] + nextw < dist[nextp]) {
dist[nextp] = dist[p] + nextw;
heap.push({dist[nextp], nextp});
st[nextp] = 1;
}
}
}
}
long long minimumWeight(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, int src1, int src2, int dest) {
memset(dist1, 0x3f, sizeof dist1);
memset(dist2, 0x3f, sizeof dist2);
memset(dist3, 0x3f, sizeof dist3);
for (int i = 0; i < edges.size(); ++ i) {
vector<int> the = edges[i];
int a = the[0], b = the[1], w = the[2];
head[a].push_back({w, b});
back[b].push_back({w, a});
}
dijkstra(n, src1, head, dist1);
dijkstra(n, src2, head, dist2);
dijkstra(n, dest, back, dist3);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++ i) {
if (dist1[i] == INF || dist2[i] == INF || dist3[i] == INF) continue;
res = min(res, dist1[i] + dist2[i] + dist3[i]);
}
return res == INF ? -1 : res;
}
};
L3-028 森森旅游 (30 分)
tip
和上面那题一样,双向单源最短路
multiset:维护一个有序序列(从小到达) set:如果用它,必须存 PII 以区分相同的元素
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<LL, int> PII;
#define x first
#define y second
const LL N = 100010, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
vector<PII> head[N], back[N];
LL dist1[N], dist2[N];
bool st[N];
LL change[N];
int n, m, q;
void dijkstra(int start, vector<PII> * node, LL * dist) {
memset(st, 0, sizeof st);
priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII>> heap;
dist[start] = 0;
st[start] = 1;
heap.push({0, start});
while (heap.size()) {
PII the = heap.top();
heap.pop();
int p = the.y, w = the.x;
if (st[p] == 0) continue;
st[p] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < node[p].size(); ++ i) {
int nextp = node[p][i].y, nextw = node[p][i].x;
if (dist[p] + nextw < dist[nextp]) {
dist[nextp] = dist[p] + nextw;
heap.push({dist[nextp], nextp});
st[nextp] = 1;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
// freopen("1.txt", "r", stdin);
memset(dist1, 0x3f, sizeof dist1);
memset(dist2, 0x3f, sizeof dist2);
cin >> n >> m >> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++ i) {
int a, b, w, t;
cin >> a >> b >> w >> t;
head[a].push_back({w, b});
back[b].push_back({t, a});
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
cin >> change[i];
}
dijkstra(1, head, dist1);
dijkstra(n, back, dist2);
multiset<LL> S;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) {
if (dist1[i] == INF || dist2[i] == INF) continue;
S.insert(dist1[i] + dist2[i] / change[i] + (dist2[i] % change[i] ? 1 : 0));
}
for (int j = 1; j <= q; ++ j) {
LL i, newVal; cin >> i >> newVal;
if (dist1[i] != INF && dist2[i] != INF) {
LL old = dist1[i] + dist2[i] / change[i] + (dist2[i] % change[i] ? 1 : 0);
S.erase(S.find(old)); // 必须用 find,如果有重复的值,会一起删除
change[i] = newVal;
LL newRes = dist1[i] + dist2[i] / change[i] + (dist2[i] % change[i] ? 1 : 0);
S.insert(newRes);
}
cout << *S.begin() << endl;
}
return 0;
}